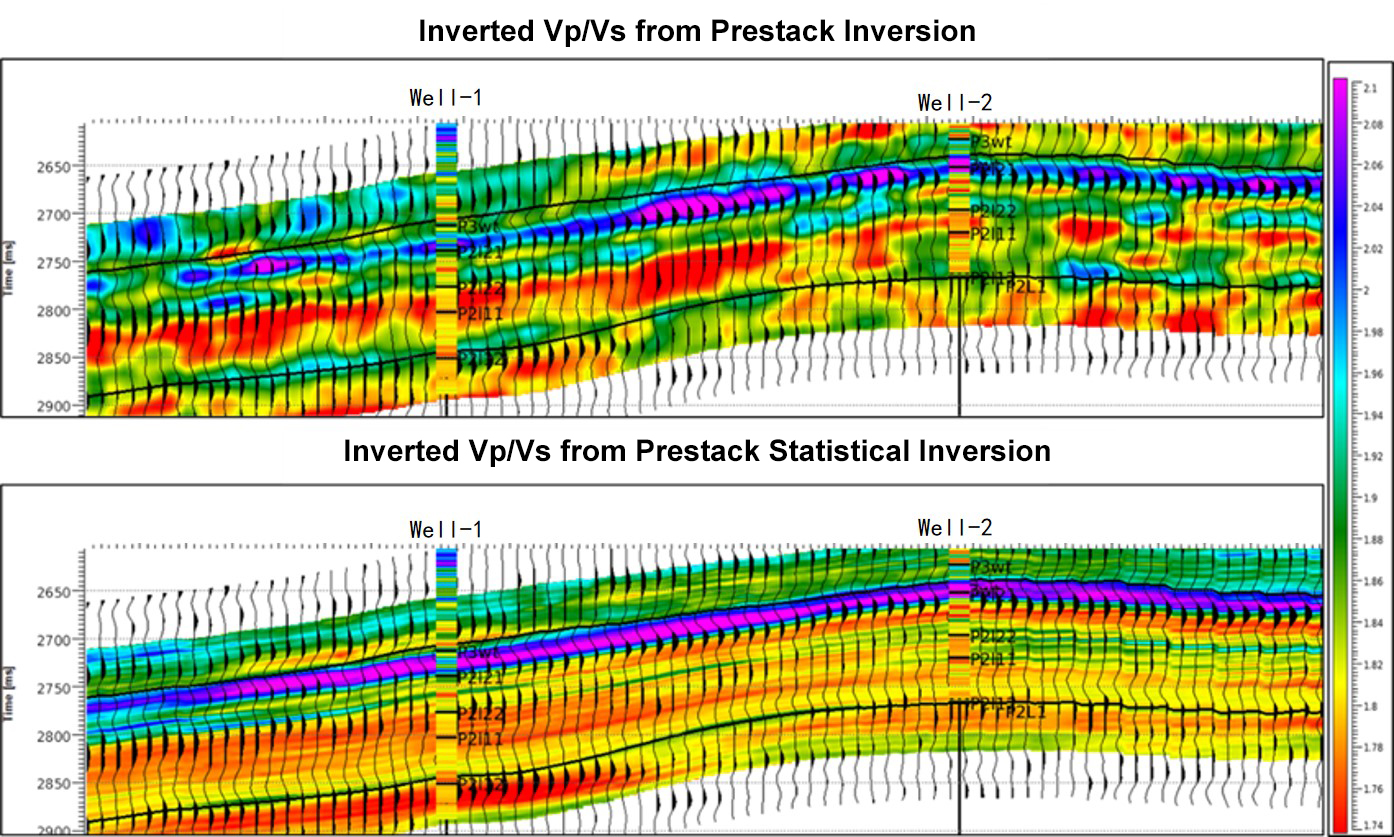
Prestack geostatistical inversion
Prestack geostatistical inversion uses the rigorous Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), which combines constrained sparse pulse inversion and stochastic simulation techniques to form a new random inversion algorithm. A rigorous probability distribution model is defined by combining information such as seismic lithofacies, logging curves, probability density functions, and variation functions. First, the probability density function and variation function are obtained through the analysis of logging data and geological information; secondly, the complex MCMC method obtains a statistically correct set of sample points according to the probability distribution function (PDF). That is, what type of results can be obtained according to the probability distribution function and the built-in constraint sparse pulse inversion engine ensures that the effective bandwidth of seismic data. Since geostatistics inversion provides a large number of details that exceed the bandwidth of seismic data, and the trend is exactly the same as the seismic data, which makes a perfect balance between qualitative waveform interpretation and quantitative reservoir interpretation based on modern karst theory.
Prestack geostatistical inversion mainly solves the following problems
- Thin layer problem below seismic resolution
- Solve the problem of lithological multi-solution of overlapping single seismic attribute
- Used to build static models of reservoirs